Varicose veins: a widespread disease
You hold (is) primitive varicose veins? This disease is widespread and affects approximately 10% of the adult population. Its origin is unclear, several factors intervene pretend :
- Hereditary metabolic disease tissue constituting the vein wall
- Exposed occupation (standing)
- Overweight
- Pregnancy
- Hormone treatments
- Heat (floor heating, bakery, laundry ...)
- Physical inactivity
- Certain sports (tennis, squash, jogging, weight training ...)
- Environments
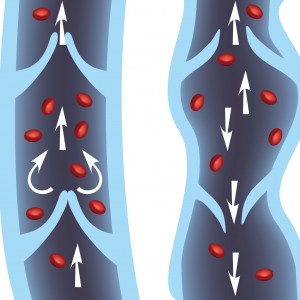
The duct is a tube which returns the blood from the bottom (feet) above (groin) by a low pressure system using muscle contractions. Between each contraction a valve system prevents the blood back down to the foot.
Varicose veins are due to an anomaly in the wall of the vein, which leads to malfunction of the valves, then the blood flowing from top to bottom towards the feet.

The lower limbs
- A deep system against bones and arteries that is the major blood transport system and is not affected by the disease
- An additional superficial system of precedent and that can be achieved. This system comprises :
- The great saphenous vein from the inside of the ankle and back to the inner leg and thigh to throw in the groin
- The small saphenous vein which starts from the outside of the ankle, following the back of the leg to throw behind the knee
- various other veins :
- Previous saphenous
- Posterior saphenous
- Saphenous accessory
- Marginal
- Communicating
- Piercing
Symptoms
Symptoms vary :
- Aesthetic inconvenience with apparent major vein or increase volume providing a relief on the surface of the skin
- Leg heaviness (lead leg), restlessness, tingling in the legs
- Edema, or swollen leg
- Bleeding in places in impact arrested by compression
- Pain on the route of the vein
- Paraphlébite (the path of the vein is painful inflammatory red and hard, witnessed the blood is coagulated in the vein)
- etc..
A Doppler ultrasound should be performed by a physician experienced in the exploration of the superficial veins
Treatment
The treatment may be :
- Medical :
- Of life hygiene
- Port contention
- Sclerosis
- Veinotonic ...
- Surgical :
- It is usually outpatient treatment
- It can combine several techniques :
- The endovenous techniques: laser or radiofrequency :
- They appeared a few years ago
- They are to leave the veins in place and treat the amount within a fiber with a thermal effect
- These techniques allow a recovery much faster than conventional techniques activities
- They are not currently reimbursed by social security and can be supported by your mutual
- Micro-invasive techniques :
- Stripping or stripping :
- They consist in removing the diseased vein segment through an incision on both sides
- The incisions are very small on the order of a centimeter
- Most often a rigid guardian used within the vein
- It is the reference technique
- Phlebectomy Müller :
- This is to remove the short segment vein by short segment
- Is performed by a few mm micro incision using hooks Müller
- Stripping or stripping :
- The endovenous techniques: laser or radiofrequency :
The suites
Postoperative Suites :
- There is no son to withdraw, they are placed in the skin and they resolve spontaneously. On all micro incisions Steri-strips were introduced. they must be kept for 8 days. If one of them fell during this period, you will have to replace those that have been prescribed
- An elastic restraint is to be applied for 1 to 2 months (tape and bottom). It must be set up in the morning and removed at night before bed
- Showers are authorized third day, however the baths are banned for 3 weeks
- The waning of the intervention of the hematoma will appear, especially on the thighs. They disappear in about 1 month; beyond persist cords on the path of the removed veins or swellings facing incisions. These elements disappear spontaneously in 6 to 8 weeks. Pain against these hematomas are more or less important, anti-inflammatory ointment and analgesics were commanding you to calm
- You can walk as much as you want, but you must avoid trampling
- However, do not allow yourself any sporting activity for 3 weeks
- Sitting, the legs should be elevated and night it is desirable to raise the foot of the bed of 5 cm. However, do not put pillow under your legs
- A phlebological monitoring will be required after the procedure
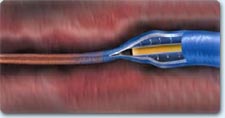
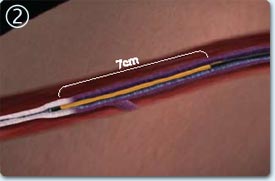
Endovenous treatment
The catheter is introduced into the vein

The vein heaters and sinks

The catheter is removed, closing the vein
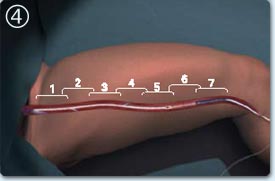
Example venous treatment: single segmental ablation
The end of the catheter is positioned 2 cm downstream of the saphenofemoral junction of tumescent liquid is administered around the saphenous vein in the compartment.
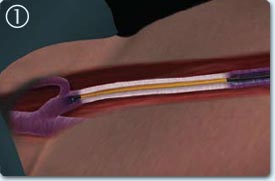
The trademarks of the catheter shaft allows quick and precise repositioning of the catheter between treatment cycles, no energy is delivered during the repositioning.
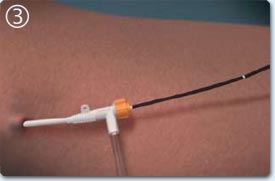
A segment of 7 cm vein is treated at one time during a 20 second processing cycle, additional vein segments are processed successively.
Treatment with a length of 45 cm vein takes 3 to 5 minutes (7 segments of treatment).